Starting a trailer rental business can be a lucrative venture for entrepreneurs looking to tap into the transportation and logistics industries.
Whether it’s for hauling goods, transporting equipment, or moving personal belongings, trailers serve a variety of purposes, making them a valuable asset in numerous sectors.
If you’re considering venturing into this business, here’s a comprehensive guide on how to get started.
Our Verdict
- Know your market: Research local demand - construction, landscaping, or homeowner needs.
- Hire and train your crew properly.
- Pick the right trailers: Focus on utility trailers or cater to specific needs (enclosed, car haulers).
- Get the proper maintenance tools and accessories.
- Register with the proper legal authorities.
- Invest in trailer rental software for security and tracking.
- Buy trailers in a huge number before starting.
- Skip insurance: Get proper liability and cargo insurance to protect yourself.
- Have an untrained crew.
- Compromise on customer safety.
Understanding the Trailer Rental Business
Before diving into the specifics, it’s essential to grasp the fundamentals of the trailer rental business. This includes understanding market demand, identifying potential customers, and assessing the competition.
Conduct thorough research to gain insights into the industry landscape and determine the viability of your business idea.
Make sure you have a good sense of sizes, capacity, and trailer types before you acquire a fleet. By knowing your audience, you can decide what kind of trailer would suit their needs best.
Consider your geography and demographics for a better grasp of customer needs.
While densely populated areas and big cities may indicate higher demand for utility trailer rentals, rural areas also present a substantial market.
In the countryside, utility trailers are commonly used to transport feed, livestock, farm equipment, and other supplies, making them essential for agricultural and rural community needs.
Benefits of Starting a Trailer Rental Business
Steady Income Stream: Reliable demand for trailers for moving, transporting, and recreational purposes can ensure consistent revenue.
Lower Initial Investment: Trailers are generally less expensive compared to other types of rental equipment, reducing the initial financial outlay.
High Demand for Short-Term Use: Many people and businesses prefer renting trailers for short-term needs rather than investing in ownership.
Diversification Opportunities: Offer a variety of trailers (e.g., cargo, utility, RV) to cater to different customer needs, increasing market reach.
Minimal Maintenance Costs: Trailers typically have lower maintenance and repair costs compared to other rental equipment, making them cost-effective to manage.
Low Overhead Costs: With minimal staffing requirements and a straightforward operational model, overhead costs remain relatively low.
Required Equipment and Average Cost
Starting a trailer rental business requires a variety of equipment and resources. Below is a comprehensive list of the necessary items along with their average costs:
- Trailers:
- Utility Trailers: $2,000 $5,000 each
- Enclosed Cargo Trailers: $3,000 $10,000 each
- Car Hauler Trailers: $4,000 $8,000 each
- Flatbed Trailers: $5,000 $15,000 each
- Dump Trailers: $6,000 $12,000 each
- Specialty Trailers (e.g., bike trailers, boat trailers): $3,000 $15,000 each
- Office Space:
- Rental of a Small Office or Lot: $500 $2,000 per month
- Office Equipment:
- Computer and Printer: $500 $1,500
- Office Furniture (desk, chairs, filing cabinets): $500 $2,000
- Phone System: $200 $600
- Internet Service: $50 $100 per month
- Management Software:
- Rental Management Software: $50 $200 per month
- Insurance:
- Commercial Insurance: $1,000 $5,000 annually
- Licensing and Permits:
- Business License and Permits: $100 $500 (varies by location)
- Security Systems:
- Surveillance Cameras: $500 $2,000
- Alarm System: $200 $1,000
- Maintenance Equipment:
- Basic Tools and Equipment: $200 $1,000
- Trailer Repair Tools and Parts: $500 $2,000
- Marketing and Advertising:
- Website Development: $500 $5,000
- Online Marketing (SEO, Google Ads, Social Media Ads): $200 $1,000 per month
- Printed Materials (brochures, business cards): $100 $500
- Signage:
- Business Sign: $200 $1,000
- Vehicle for Transporting Trailers (if needed):
- Pickup Truck or SUV: $20,000 $50,000
Summary of Initial Setup Costs:
- Trailers: $30,000 $100,000 (assuming a variety of 10 trailers)
- Office Space: $500 $2,000 per month
- Office Equipment: $1,200 $3,500
- Management Software: $50 $200 per month
- Insurance: $1,000 $5,000 annually
- Licensing and Permits: $100 $500
- Security Systems: $700 $3,000
- Maintenance Equipment: $700 $3,000
- Marketing and Advertising: $800 $6,500 initially, plus monthly costs
- Signage: $200 $1,000
- Vehicle for Transporting Trailers: $20,000 $50,000
Estimated Total Initial Setup Cost:
Approximately $55,250 to $174,700 (excluding monthly operational costs and assuming the purchase of 10 trailers).
Keep in mind that these costs can vary widely based on location, the scale of the business, and specific market conditions.
Market Research and Analysis
Begin by conducting market research to identify your target market and assess their needs and preferences. Analyze competitors to understand their offerings, pricing strategies, and customer base. This information will help you tailor your services to meet the demands of your target audience effectively.
Trends in the Trailer Rental Industry
Due to their cost-effectiveness, many companies are beginning to opt for trailer rentals instead of buying them.
Trailers are becoming popular, not just for commercial use but also for personal use. There’s visible growth in the market.
The trailer rental business requires long-term capital investment; the payback period is long, resulting in a highly competitive market.
Many startups acquire only one rental trailer instead of a full-blown business, resulting in a higher local concentration of trailer rental businesses.
Business Planning
Formulate a comprehensive business plan outlining your goals, objectives, and strategies for success. Determine the initial investment required, projected expenses, and revenue targets. A well-thought-out business plan will serve as a roadmap for your venture and guide your decision-making process.
Business Goals and Objectives
Define your overarching goals, such as becoming a prominent player in the trailer rental industry or providing trailer services locally.
Set specific objectives, such as achieving a certain market share within a defined timeframe or renting out a specific number of trailers annually.
Business Model
Decide whether you’ll have an online booking system or rent out locally. Determine the types of trailers you’ll offer for rent and the target market you’ll cater to.
Consider the pricing strategy, distribution channels, and marketing plans to attract people.
Understand the distinction between company and business to make sure you comply with all legal requirements when selecting a business structure.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Research and understand the legal requirements and regulations governing trailer rental businesses in your jurisdiction.
Obtain the necessary licenses, permits, and approvals before launching your business.
Security and Transparency
Implement robust security measures to safeguard against theft and financial damage.
Make sure you keep track of your customers and rent your trailers to people who have the right qualifications.
Payment Methods
If you have an online rental system, offer multiple payment methods to cater to diverse customer preferences, such as credit/debit cards, bank transfers, and digital wallets.
Ensure secure payment processing and compliance with financial regulations.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Monitor KPIs such as net profit, revenue growth, customer retention rates, and cost per acquisition.
Use KPIs to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of your online booking system and make data-driven decisions for optimization.
Market Analysis and Competition
Conduct a thorough analysis of the trailer rental market by using Porter’s Five Forces and digital tools for competition analysis.
Assess competition dynamics, identify key players, and analyze their strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. Develop competitive advantages and differentiation strategies to carve out a unique position in the trailer rental market.
This list is by no means exhaustive and can be expanded based on business needs. For instance, you might want to consider your geographical advantage or disadvantage before deciding on a business model.
For a more thorough approach with reduced hassle, consider hiring a business formation service.
Legal Requirements
Before launching your trailer rental business, ensure that you comply with all legal requirements. This includes registering your business, obtaining the necessary licenses and permits, and adhering to local regulations. Failure to comply with legal obligations can result in fines or penalties, so it’s essential to address these matters diligently.
Register Your Business
Contact the Relevant Authorities: In most states, you can register your trailer rental business by reaching out to the Secretary of State’s office, a Business Bureau, or a Business Agency.
Consider DBA Registration: If you operate under a fictitious name, also known as a DBA (Doing Business As), some states may require you to register it. Check local government regulations to determine if DBA registration is necessary.
Check State Tax Requirements: After registering your business, verify if you need to comply with your state’s tax board or franchise tax board regulations. This may involve filing Initial Reports within 90 days of registration, depending on your business structure.
File Necessary Reports: Ensure timely filing of Initial Reports, typically required within 90 days of business registration. However, exemptions may apply based on your business structure.
Choose the Right Business Structure: Before registration, decide on the appropriate business structure that aligns with the goals and needs of your trailer rental business. Options may include sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC (Limited Liability Company), or corporation.
Register as a Taxpayer
Get an Employer Identification Number: You’ll need to order an EIN (Tax ID Number), which is required to identify your business as a tax-paying entity.
Obtain a Sales Tax License: Acquire a Sales Tax License or seller’s permit to collect sales tax from customers and report these amounts to the state regularly. You can obtain this permit from your Secretary of State’s office, typically without incurring fees.
When seeking a sales tax license, you are required to complete an application form that asks for details regarding their business, including its structure, name, address, and contact information.
Moreover, the business proprietor may be required to present their Social Security number or EIN, along with specifics regarding the products or services offered by the business.
Check with your state’s sales tax agency to confirm what you are required to do.
Get Licenses and Permits
Check local government websites to determine the licenses needed to operate your trailer rental business. These may include:
Vehicle Permits: Depending on your state, you may need vehicle permits, along with a valid driver’s license and clean driving record.
Trailer Rental License: Not all states require rental licenses for trailer leasing businesses. Visit your state government’s website for specific regulations.
Consider DBA Registration: If you operate under a fictitious name, also known as a DBA (Doing Business As), some states may require you to register it. Check local government regulations to determine if DBA registration is necessary.
Zonal Permit: Zoning permits are required when the status (or use) of a building is changed. Renovation or remodeling aren’t necessary. If the purpose of the property is changed, a zoning permit will be required. Apply through local government offices, providing necessary documents and fees.
Signage Permit: Obtain a permit for business signage after acquiring a zoning permit. Provide details about the sign’s dimensions, materials, and location.
Choosing the Right Trailers
Selecting the right trailers for your business is crucial to its success. Assess different types of trailers, such as utility trailers, flatbed trailers, and enclosed trailers, based on their demand and suitability for various purposes. Consider factors such as durability, size, and features when making your selection.
Choosing the right trailers means creating a diverse fleet that has many types of trailers for different purposes.
Types of Trailers
There are over 20 types of trailers. It’s nearly impossible to keep track of all the names that some trailers are known by. Here are a few of the most important ones you’ll need to know about.
Standard Flatbed Trailers:
Flatbed trailers are highly versatile and widely used for their convenient loading and unloading capabilities from each side. With no roof or enclosure, they offer a long, level surface, making it easy to accommodate a variety of freight.
Available in different sizes, flatbeds provide flexibility to better suit your cargo needs.
Dump Trailers:
Dump trailers, designed for transporting waste and debris, are available in a range of sizes and axle configurations, offering different hitch and gate styles.
Certain companies offer details such as the trailer’s gross vehicle weight rating, trailer weight, or maximum payload capacity, aiding in selecting the most suitable and secure trailer for your hauling requirements.
Gooseneck Trailers:
Gooseneck trailers feature a hitch that extends upward and outward from the hauling vehicle.
This hitch connects to a ball mount installed within the bed of the hauling truck. Typically, the ball mount is affixed to the frame of the truck and positioned above the rear axle of the vehicle, ensuring exceptional stability while driving.
Refrigerated Trailers (Reefers):
Refrigerated trailers, also known as reefers, play a vital role in modern food supply chains, offering temperature control for goods that are sensitive to temperature fluctuations.
These insulated, sealed units are essential for protecting perishable items during transportation. Even items like certain fruits, which may be safe over short distances, require the advanced temperature regulation provided by reefers for long-distance hauls.
Landscaping Trailers:
Landscape trailers are designed for hauling landscaping materials such as yard waste, tools, or chemicals. Some feature specialized tools and layouts to transport equipment efficiently. Organized compartments for different devices can simplify the transportation of lawn equipment.
Additionally, landscape trailers can accommodate powersport equipment and small vehicles like ATVs, dirt bikes, or side-by-sides.
Location and Maintenance
Securing a suitable location for your trailer rental business is paramount. Choose a location with high visibility and easy access for customers. Additionally, invest in maintenance and storage facilities to ensure that your trailers are well-maintained and secure when not in use.
It is especially important for bigger trailer rentals to secure a good location for their business. Many smaller rentals that are closer to residential areas are preferred for personal use instead of bigger trailer rentals that are located far away.
Trailer rentals that are close by are also cost-effective, making them a better option in most cases.
Having an office and a secure space for trailers is important. You’ll be managing all your accounts, bookings, and other official processes through your office. Keeping track of which trailers need maintenance is also important.
While trailers are built to be sturdy, depending on the kind of trailer, you might need to invest in proper maintenance.
Marketing and Promotion
Create a strong brand identity for your trailer rental business and implement effective marketing strategies to attract customers.
Utilize a mix of online and offline marketing channels, such as social media, advertising, and networking events, to promote your services and reach your target audience.
There are a couple of ways to promote your trailer rental business.
Invest in a Website
Online bookings are more popular than those done in person. Having a website gives your business digital visibility. Even if you don’t have an online booking system, having a website is a great way to market yourself.
Having information like pricing, contact information, availability, address, etc. can make your website useful to your customers.
Hiring someone to do SEO for your website will help ensure that it is visible to users and reach people who are interested in renting a trailer.
Establish Social Media Presence
Social media platforms provide excellent opportunities to increase visibility. Promote your trailer rental across social media channels and track audience engagement.
Analyze traffic patterns and engagement metrics to inform your marketing strategy and future business decisions.
Invest in Paid Advertising
Investing in paid advertising involves running campaigns on social media platforms and search engines. As online rental and booking systems dominate, paid ads can significantly expand your reach and attract more customers.
Financial Management
Effective financial management is crucial for the long-term success of your trailer rental business. Keep track of expenses and revenue, and implement budgeting and accounting practices to ensure profitability. Consider offering flexible pricing options and discounts to attract customers and maximize revenue.
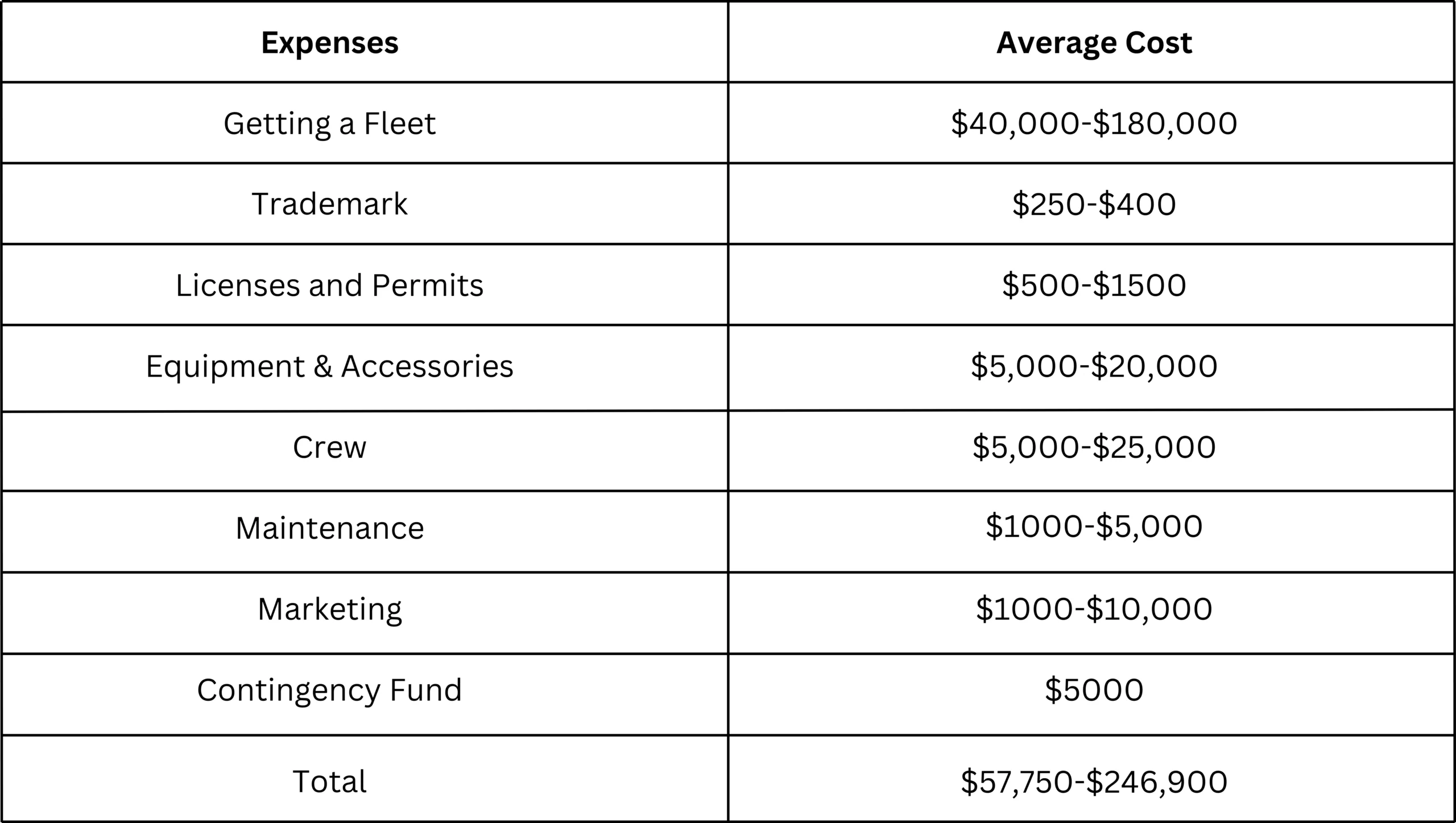
Budget and Pricing for a Trailer Rental Business
The rental cost of trailers varies depending on the style, ranging from $30 to $200 per day. This cost depends on the kind of trailer you are renting out.
The cost of trailers varies depending on what kind they are. For instance, you can expect to find a car hauler trailer at the price of $4,500 on average. A gooseneck trailer is nearly double at $9,600 on average. While a simpler utility trailer is half the cost of a car hauler at about $2,400 on average,.
Unless you only plan to buy one trailer, you will likely be buying more than one type of trailer. Plan your fleet according to your budget.
Licenses and permits can cost varying amounts across different states, but you can expect to pay at most $1500. If you choose to trademark your business, that may cost even more.
Marketing can cost about $5000 or more, depending on the scope of your campaign.
Office expenses, renovations, and other legal fees can cost from $5000 to $10,000 or more.
For a better result, calculate your business expenses here:
Budget Calculator
Insurance Coverage
Obtain insurance coverage for your trailers and business liability to protect against unforeseen circumstances. Work with an insurance provider to assess your coverage needs and obtain the necessary policies to safeguard your assets and mitigate risk.
Liability insurance offers protection against claims arising from injuries and property damage. It covers legal expenses and payouts for which the insured party is deemed liable. However, it typically excludes intentional damage, contractual liabilities, and criminal prosecution from its coverage.
Any rental business that deals with vehicles of such a scale should get liability insurance.
Safety Regulations
Ensure that your trailer rental business complies with all safety regulations and standards. Implement safety protocols for customers, including proper loading and securing of cargo, and conduct regular maintenance checks on your trailers to ensure they are in optimal condition.
If you have hired staff, make sure they are trained in handling the trailers. Keeping your trailers in proper shape by ensuring maintenance is important.
Make sure the renters have a driving license before you rent your trailers out.
Check out the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration’s safety regulations to ensure your trailer rental business follows all the requirements.
Conduct monthly business reviews to ensure your finances are on the right road and plan accordingly.
FAQs
1. What types of trailers are most in demand for rental businesses?
Utility trailers, enclosed trailers, and flatbed trailers are among the most popular choices for rental businesses, catering to various transportation needs.
2. How much does it cost to start a trailer rental business?
The initial investment can vary depending on factors such as the number of trailers, location, and facilities. It’s essential to create a detailed business plan to estimate startup costs accurately.
3. Do I need special insurance for my trailer rental business?
Yes, it’s essential to obtain insurance coverage for your trailers and business liability to protect against potential risks and liabilities.
4. How can I attract customers to my trailer rental business?
Implementing effective marketing strategies, providing exceptional customer service, and maintaining a strong online presence can help attract customers to your trailer rental business.
5. What are some common challenges faced by trailer rental businesses?
Common challenges include competition from established rental companies, fluctuating demand, and regulatory compliance. However, with careful planning and strategic management, these challenges can be overcome.
6. What do I need to start a trailer rental business?
To start a trailer rental business, you need a fleet of well-maintained trailers, a reliable rental management system to track reservations and payments, and a solid marketing strategy to attract customers. Additionally, ensure you have appropriate insurance and legal compliance in place for your operations.
7. Is renting trailers a good business?
Renting trailers can be a profitable business due to high demand for transportation and storage solutions. It offers recurring revenue from rental fees and can scale with growing market needs. However, success depends on location, maintenance costs, and effective marketing strategies.


